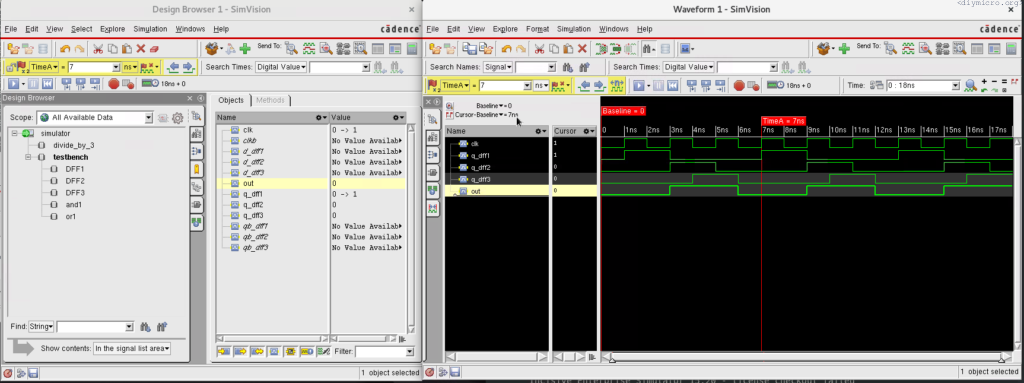
Since I already described the process in my previous post, this one is going to be much shorter.
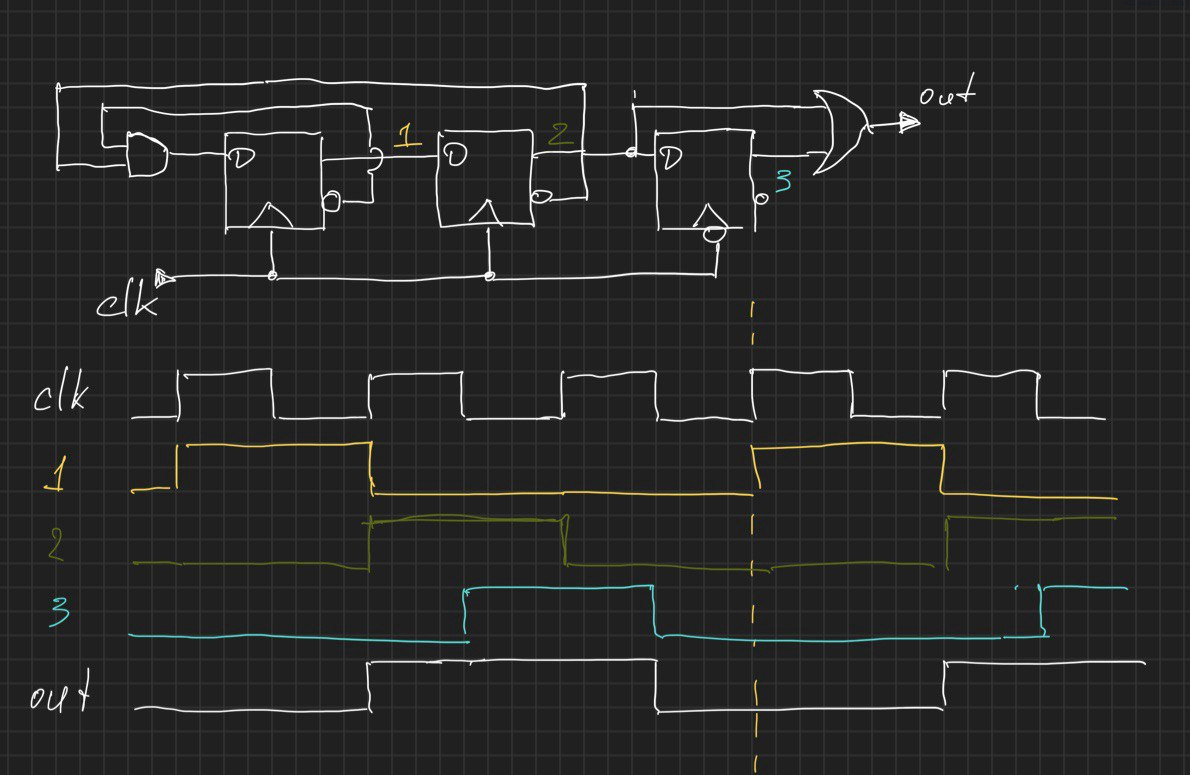
So, let’s use the same example of the divide by 3 circuit:
In the xcelium case, it is actually easier to runthe testbench somewhat if you are comfortable with the command line interface (CLI):
xrun testbench_sandbox.sv design_sandbox.sv -access +rwc -gui The verilog code is exactly the same as it was in the aforementioned post, but I’m repeating that again.
The module code:
//sandbox design diymicro
module dff (clk, d, q, qb);
input clk;
input d;
output q;
output qb;
reg q;
assign qb = ~q;
initial begin
q = 1'b0;
end
always @(posedge clk)
begin
// Assign D to Q on positive clock edge
q <= d;
end
endmodule
module and_gate (input wire a,b,
output wire z);
assign z = a & b;
endmodule
module or_gate (input wire a,b,
output wire z);
assign z = a | b;
endmodule
The testbench code:
// Code your testbench here
// or browse Examples
`timescale 1ns / 1ns
module testbench();
reg clk;
wire out;
wire qb_dff1;
wire d_dff1;
wire q_dff1;
wire clkb;
wire qb_dff2;
wire d_dff2;
wire q_dff2;
wire qb_dff3;
wire d_dff3;
wire q_dff3;
assign clkb = ~clk;
dff DFF1(.clk(clk), .d(d_dff1), .q(q_dff1), .qb(qb_dff1));
dff DFF2(.clk(clk), .d(d_dff2), .q(q_dff2), .qb(qb_dff2));
dff DFF3(.clk(clkb), .d(d_dff3), .q(q_dff3), .qb(qb_dff3));
and_gate and1(.a(qb_dff1),.b(qb_dff2),.z(d_dff1));
assign d_dff2 = q_dff1;
assign d_dff3 = q_dff2;
or_gate or1(.a(q_dff3),.b(q_dff2),.z(out));
//assign d_dff1 = qb_dff1;
initial begin
$dumpfile("dump.vcd");
$dumpvars(1);
clk = 1'b0;
#18 $finish;
end
always #1 clk = ~clk;
endmodule : testbench SimVision will start after that xrun command and you will need to add waveforms of interest to the wave window and click the run button again…